The Turing machine, proposed by Alan Turing, was a theoretical computational model that laid the conceptual foundation for complex computation and problem solving. It demonstrated the possibility of solving any computable problem using simple rules and an infinite tape, and provided the theoretical basis for the design principles and algorithms of modern computers.
The computer is a unique invention with infinite possibilities. Computers have the versatility to accelerate and extend the human thought process. Whether it’s finding information on the internet, connecting friends, sending money to a bank account, predicting chemical reactions, or calculating the formation of galaxies in the universe, computers have played an important role in the development of modern civilization. Now they’re in our phones and cars, making our world more convenient everywhere.
It was British mathematician Alan Turing who proposed the fundamental design of this universal computer. Often referred to as the father of computers, Turing is remembered as an important figure in the history of computers for his work. The Computer Society honors him with the Turing Prize, which is awarded annually to someone who has made a significant contribution to the field of computing, similar to the Nobel Prize in science. It is also well known that the logo of the American company Apple, famous for revolutionizing smartphones, symbolizes the poisonous apple that Turing ate.
The Turing machine played a key role in the invention of the computer. Understanding Turing machines can help you understand how the computers that pervade society today got their start. Let’s take a closer look at what a Turing machine is, how it works, and how it contributed to the development of computers.
A Turing machine, as proposed by Turing, is an abstract machine that has no physical form. The concept was proposed by Alan Turing as part of a new proof of Gödel’s incompleteness theorem, which states that “mechanical methods alone cannot produce all the facts of mathematics”. To define what a mechanical method is, he designed a model of computation with simple components and principles of behavior.
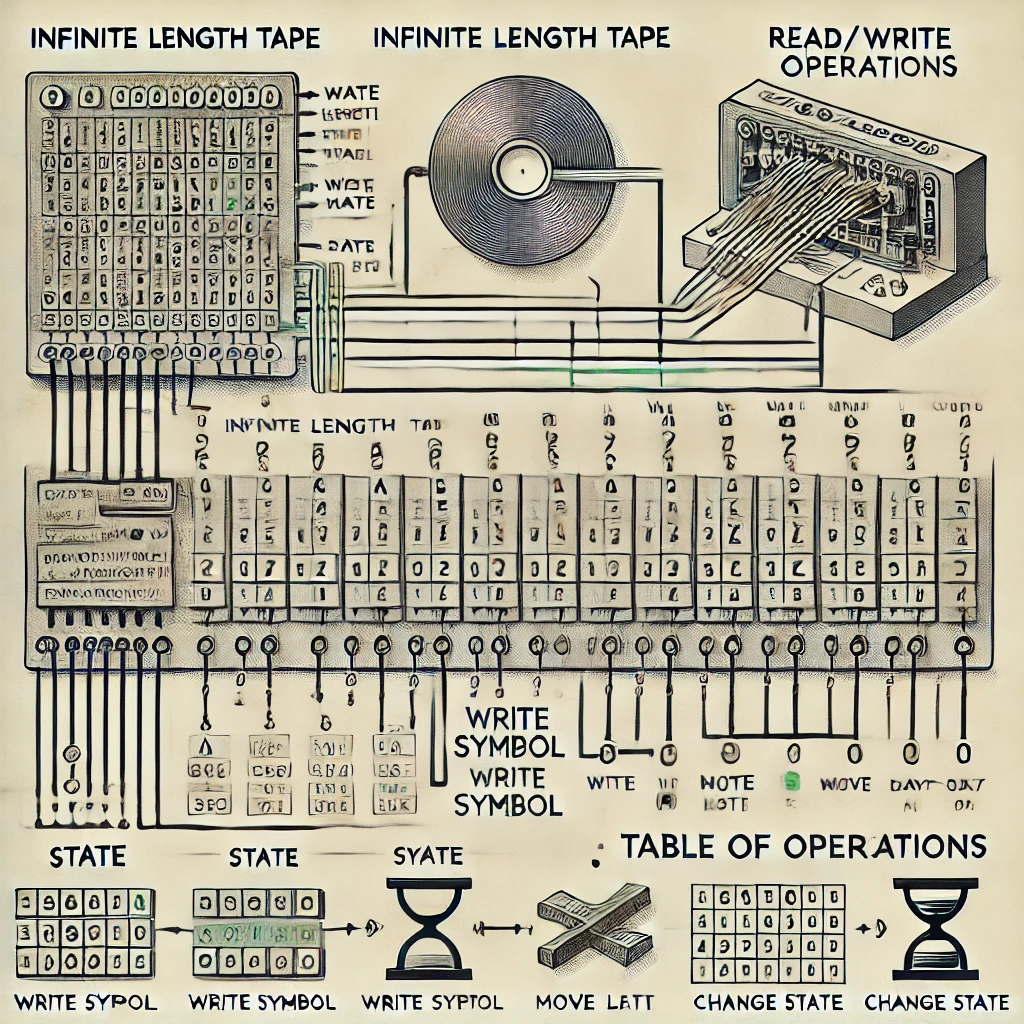
A Turing machine consists of an infinite length of tape, a reading and writing device, and a table of operating rules. The way a Turing machine works is simple. First, the read/write device reads the letters on the tape that it is currently pointing at. It then moves the reader and writer one space to the left or right, depending on the rulebook, to overwrite a new letter on the tape. For example, if the read/write device is currently pointing to the letter A, it would read A, move it one space to the right, erase the letter written there, and write a new letter, B, according to the rulebook.
What makes Turing machines so important is that they can mimic all other calculators with such simple components and behavior. Turing proved that given enough time, any kind of computation could be performed by a Turing machine that would mimic its counterpart and produce the desired result. The Turing machine was the first such universal model of computation. This gave computers the theoretical guarantee of being able to perform all kinds of computational tasks. Furthermore, Turing’s conjecture that the Turing machine is the only universal computational model remains unbroken. It has been shown that every computational model that has ever existed is reducible to a Turing machine. If it were possible to design a mechanical model of computation that could not be imitated by a Turing machine, a new concept of computer could be created.
Turing machines differ from the primitive forms of computers that came before them in that they can perform any form of logical computation. Earlier primitive computers could only perform a few predetermined calculations, such as arithmetic or solving differential equations. Turing machines, on the other hand, could imitate all other Turing machines, allowing them to perform any complex form of computation that a person wanted.
So far, you’ve learned what a Turing machine is, how it works, and what it means in computer theory. Once an abstract machine, the Turing machine was implemented into a real machine by von Neumann, another brilliant mathematician, and became the beginning of the electronic computers that are changing the world today. Since then, computers have gotten faster and more complex, but the theoretical roots of the Turing machine have always been there. Turing’s ideas, proposed to prove Gödel’s incompleteness theorem, were developed and eventually led to the information revolution.